Abstract
Background:
Bleeding and thrombosis are prevalent across all myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) subtypes and have significant impact on morbidity and mortality. Although risk factors for thrombosis are well established, bleeding risk factors in these patients are poorly characterized. Identifying MPN patients at higher risk for bleeding could guide the duration of anticoagulation for patients with MPN associated thrombosis (balancing the risk between bleeding and thrombosis), select individuals at higher risk for bleeding during prophylactic anticoagulation, and predict for bleeding complications with surgical procedures.
Methods:
We performed a retrospective analysis of bleeding risk factors among consecutive adult MPN patients treated at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center. Bleeding events were classified as minor or major events as defined by the International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostasis (ISTH). The primary outcome of interest was time to initial bleeding after MPN diagnosis. Patient characteristics were summarized as range and medians (for continuous variables) and counts with percentages (for categorical variables) (Table 1). Cox regression was used to examine the associations between candidate risk factors with identified bleeding events in univariate and multivariable analyses. Variables with p<0.1 in univariate analyses were selected for multi-variate analysis. A time-dependent variable of thrombosis status was included in the model. A stepwise feature selection based on Akaike Information Criterion was used for model selection. Continuous variables were dichotomized at median for the regression analyses.
Results:
A total of 170-consecutive adult MPN patients were identified between 2005 and 2021. Median follow-up was 43.5 months (range 0.66-485.72). The rate of bleeding (major and minor) was 4.9/100 patient-years and rate of thrombosis was 5.4/100 patient-years (5.4/100 patient-years for arterial thrombosis and 2.9/100 patient-years for venous thrombosis).
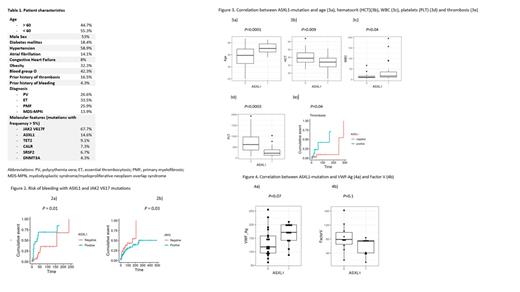
In univariable analysis, predictors of bleeding included age > 60 years (HR 2.8; 95% CI 1.47-5.34; p=0.001), diagnoses of primary myelofibrosis (PMF) (HR 2.98; 95% CI 1.29-6.9; p=0.01) and myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm (MDS-MPN) overlap syndrome (HR 4.56, 95% CI1.91-10.88; p=0.0004), prior history of thrombosis (HR 3.3, 95% CI 1.27-8.8; p=0.01) and presence of ASXL1 (HR 4.13, 95% CI 2.13-8.04; p=0.0001), JAK2 V617F (HR 0.58; 95% CI 0.31-1.08; p=0.08) and TET2 mutations (HR 3.46; 95% CI 1.5-7.9; p=0.003). In multivariate analysis, the presence of JAK2 V617F (HR 4.8; 95% CI 1-21.5; p=0.03) and ASXL1 (HR 12.7, 95% CI 1.7-93; p=0.01) mutations were associated with increased risk of bleeding (Figure 2). Patients with polycythemia vera were at lower risk of bleeding (HR -3.5, 95% CI 0-0.8; p=0.03).
Since ASXL1 mutation was associated with a higher risk of bleeding, we studied the association between ASXL1 mutation and other clinical variables. Patients with ASXL1 mutations were more likely to have a diagnosis of PMF and MDS-MPN overlap syndrome (p=0.0001), age > 60 years (p=0.0001), risk for thrombosis (p=0.04), lower hematocrit (p=0.009) and platelets (p=0.0003) but higher white blood cell count (WBC) (p= 0.04) (Figure 3). We then studied the correlation between ASXL1 mutation and factor VIII/Von Willebrand complex and factor V, the two most described abnormal coagulation factors in MPN. ASXL1 mutation was not associated with a statistically significant lower VWF Ag (p=0.07) or factor V (p=0.1) that could potentially explain the higher risk of bleeding seen with this mutation (figure 4).
Conclusion:
ASXL1 mutations are associated with a significantly higher risk of bleeding in adult MPN patients. The risk of bleeding with ASXL1 mutations was independent of prior thrombosis and was not associated with abnormalities in VWF profile or factor V. Confirmation of these findings in additional patients and studies of underlying platelet function to identify the possible mechanism of ASXL1 associated bleeding in these patients are ongoing.
Elshoury: Bristol Meyers Squibb: Other: advisory board. Thompson: Novartis/ Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Griffiths: Takeda Oncology: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Boston Biomedical: Consultancy; Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; Taiho Oncology: Consultancy, Honoraria; Apellis Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Wang: Stemline Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory board, Speakers Bureau; Mana Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Kura Oncology: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory board, steering committee, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory board; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS/Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; DAVA Oncology: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Rafael Pharmaceuticals: Other: Data safety monitoring committee; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory board; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory board; PTC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory board; Genentech: Consultancy; MacroGenics: Consultancy.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal